
Liliya I. Vinarova, Ph.D.
Interests
- In-vitro Lipid Digestion and bioavailability
- Oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs
- Surfactants and Enzymes in Detergency
- Natural surfactants in foods and detergency
Bio
Publications
Most recent publications
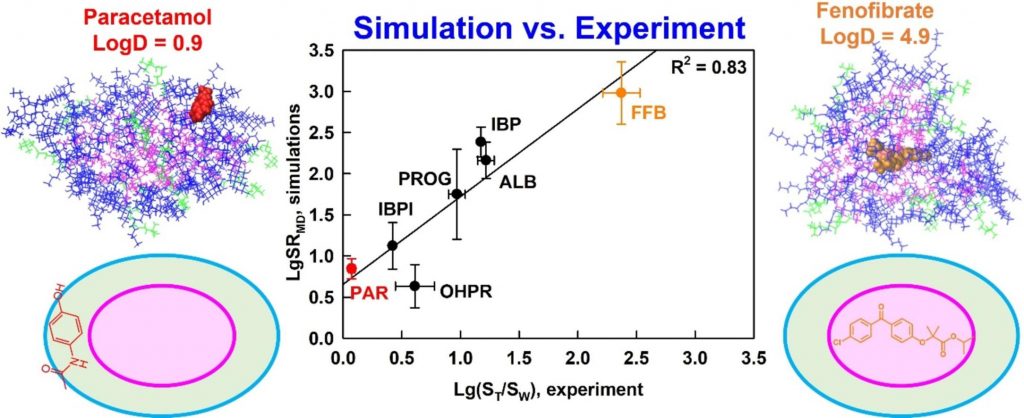
Understanding drug solubilization in intestinal mixed micelles through molecular dynamics simulations
Hypothesis
Solubilization is a fundamental process that underpins various technologies in the pharmaceutical and chemical industry. However, knowledge of the location, orientation and interactions of solubilized molecules in the micelles is still limited. We expect all-atom molecular dynamics simulations to improve the molecular-level understanding of solubilization and to enable its in silico prediction.
Methods
The solubilization of six drugs in intestinal mixed micelles composed of taurocholate and dioleoyl phosphatidylcholine was simulated by molecular dynamics in explicit water and measured experimentally by liquid chromatography. The location and orientation of the solubilized drugs were visualized by cumulative radial distribution functions and interactions were characterized by radial distribution function ratios and hydrogen bonding.
Findings
A new simulation-derived parameter was defined, which accounts for drug-micelle and drug-water interactions and correlates (R2 = 0.83) with the experimentally measured solubilization. Lipophilicity was found to govern the location of all drugs in the micelle (hydrophobic core, palisade layer or on the surface), while hydrogen bonding was crucial for orientation and solubilization of two of the molecules. The study demonstrates that explicit, hydrogen bond-forming water molecules are vital for accurate prediction of solubilization and provides a comprehensive framework for quantitative studies of drug location and orientation within the micelles.
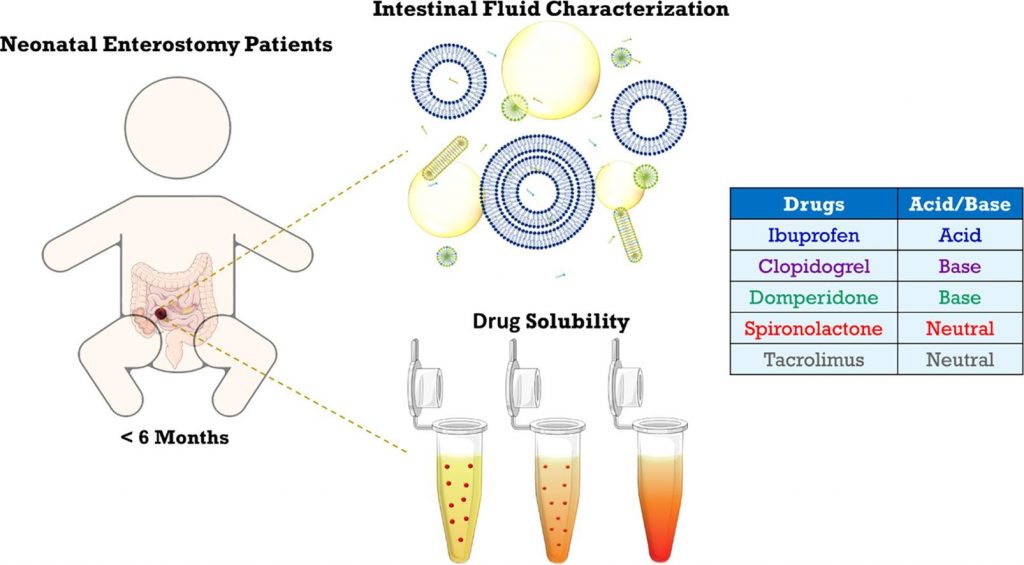
Characterization of neonatal and infant enterostomy fluids – Part II: Drug solubility
Previous research revealed marked differences in the composition of intestinal fluids between infants and adults. To explore the impact on the solubilization of orally administered drugs, the present study assessed the solubility of five poorly water-soluble, lipophilic drugs in intestinal fluid pools from 19 infant enterostomy patients (infant HIF). For some but not all drugs, the average solubilizing capacity of infant HIF was similar to that of HIF obtained from adults (adult HIF) in fed conditions. Commonly used fed state simulated intestinal fluids (FeSSIF(-V2)) predicted fairly well drug solubility in the aqueous fraction of infant HIF, but did not account for the substantial solubilization by the lipid phase of infant HIF. Despite similarities in the average solubilities of some drugs in infant HIF and adult HIF or SIF, the underlying solubilization mechanisms likely differ, considering important compositional differences (e.g., low bile salt levels). Finally, the huge variability in composition of infant HIF pools resulted in a highly variable solubilizing capacity, potentially causing variations in drug bioavailability. The current study warrants future research focusing on (i) understanding the mechanisms underlying drug solubilization in infant HIF and (ii) evaluating the sensitivity of oral drug products to interpatient variations in drug solubilization.
The mechanism of lowering cholesterol absorption by calcium studied by using an in vitro digestion model
Studies in humans show that a calcium-enriched diet leads to lower cholesterol in blood serum. This phenomenon is usually explained in the literature with a reduced cholesterol absorption in the small intestine. Our study aims to clarify the effect of calcium on the solubilisation of cholesterol and fatty acid in the dietary mixed micelles (DMM), viz. on the bioaccessibility of these lipophilic substances in the gut. We use an in vitro digestion model which mimics very closely the intestinal pH-profile and the composition of the intestinal fluids. We quantified the effects of Ca2+ concentration on the lipid solubilization for fats and oils with different saturated/unsaturated fatty acid (FA) contents. We found that the increase of calcium significantly decreases the solubilization of cholesterol, FA and MG. Most importantly, we observe a clear positive correlation between the amounts of solubilized cholesterol, on one side, and solubilized free fatty acids and monoglycerides, on the other side. The main conclusion is that Ca2+ ions strongly affect the bioaccessibility of both cholesterol and saturated FA. Therefore, calcium may decrease the serum cholesterol via two complementary mechanisms: (1) fatty acid precipitation by calcium ions reduces the solubilisation capacity of the DMM, thus decreasing the levels of solubilised (bioaccessible) cholesterol; (2) the observed strong decrease of the bioaccessible saturated FA, in its own turn, may suppress the cholesterol synthesis in the liver.
Lowering of cholesterol bioaccessibility and serum concentrations by saponins: In vitro and in vivo studies
Using an in vitro digestion model, we studied the effect of six saponin extracts on the bioaccessibility of cholesterol and saturated fatty acids (SFAs). In the absence of saponins, around 78% of the available cholesterol was solubilized in the simulated intestinal fluids. The addition of two extracts, Quillaja Dry (QD) and Sapindin (SAP), was found to decrease cholesterol bioaccessibility to 19% and 44%, respectively. For both extracts, the main mechanism of this effect is the displacement of cholesterol molecules from the bile salt micelles, leading to formation of cholesterol precipitates that cannot pass through the mucus layer of the intestine. QD decreased strongly the SFA bioaccessibility as well, from 69 to 9%, due to formation of calcium-SFA precipitates, while SAP had no effect on SFA. We studied the in vivo activity of QD and SAP extracts by measuring serum cholesterol in mice fed with experimental diets within a 7-day period. Both extracts were found to prevent dietary hypercholesterolemia in mice fed on a cholesterol-rich diet. The other saponin extracts did not show any significant effect in vitro and, therefore, were not studied in vivo. The cholesterol lowering ability of Sapindin extract is reported for the first time in the current study. This journal is
Mechanisms of cholesterol and saturated fatty acid lowering by Quillaja saponaria extract, studied by in vitro digestion model
Quillaja saponin extracts are known to reduce plasma cholesterol levels in humans. Here we study the mechanism of this effect with Quillaja Dry saponin extract (QD). In vitro model of triglyceride lipolysis is used to quantify the effect of QD on the solubilization of cholesterol and of the lipolysis products (fatty acids and monoglycerides) in the dietary mixed micelles (DMM). We found that QD extract decreases significantly both the cholesterol (from 80% to 20%) and saturated fatty acids (SFA, from 70% to 10%) solubilised in DMM. Series of dedicated experiments prove that QD may act by two mechanisms: (1) direct precipitation of cholesterol and (2) displacement of cholesterol from the DMM. Both mechanisms lead to increased cholesterol precipitation and, thus, render cholesterol bio-inaccessible. We prove also that the saponin molecules are not the active component of QD, because highly purified Quillaja extract with very similar saponin composition does not exhibit cholesterol-lowering or SFA-lowering effect. The effect of QD extract on cholesterol solubilisation is most probably caused by the high-molecular weight polyphenol molecules, present in this extract. The reduced SFA solubilisation is caused by Ca2+ ions of relatively high concentration (1.25 wt%), also present in QD extract, which precipitate the fatty acids into calcium soaps.

