Assist. Prof. Vladimir Petkov, Ph.D.
Interests
- Solubility in surfactant solutions
- Foams and antifoams
Publications
Most recent publications
ISCOM-type matrix from beta-escin and glycyrrhizin saponins
Background and aims
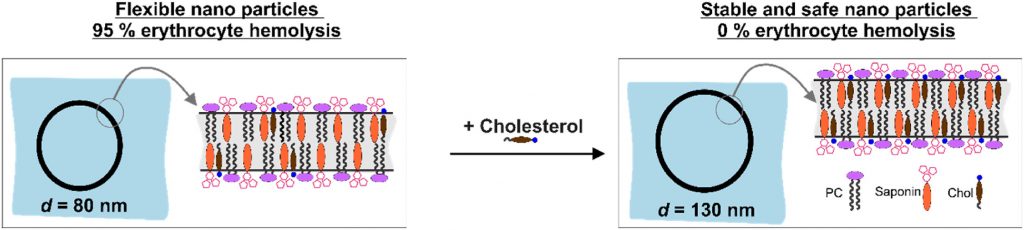
Nanotechnology provides the opportunity for construction of modern transport devices such as nanoparticles for a variety of applications in the field of medicine. A novel experimental protocol for the formation of saponin-cholesterol-phospholipid nanoparticles of vesicular structure has been developed and applied to prepare stable nanoparticles using escin or glycyrrhizin as saponins.
Methods
The methods for nanoparticle construction include a sonication at 90 °C of the initial mixture of components, followed by an additional sonication on the next day for incorporation of an additional amount of cholesterol, thus forming stable unilamellar vesicles. Tests and assays for cell viability, erythrocyte hemolysis, flow cytometry, and fluorescent microscopy analyses have been performed.
Results
By selecting appropriate component ratios, stable and safe particles were formulated with respect to the tested bio-cells. The prepared nanoparticles have mean diameter between 70 and 130 nm, depending on their composition. The versatility of these nanoparticles allows for the encapsulation of various molecules, either within the vesicle interior for water-soluble components or within the vesicle walls for hydrophobic components. The saponin particles formed after cholesterol post-addition (E3-M2) are stable and 100 % of the cells remain viable even after 10-times dilution of the initial particle suspension. These particles are successful included into isolated mouse macrophages.
Conclusions
Among the variety of generated nanoparticles, the E3-M2 particles demonstrated properties of safe and efficient devices for future vaccine design and antigen targeting to immune system.
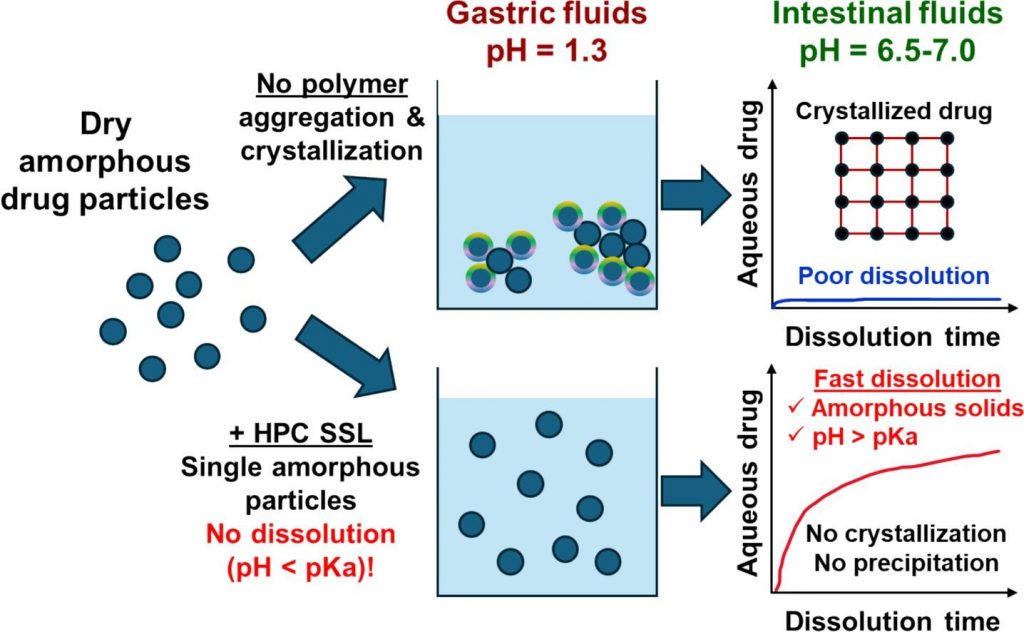
Mechanisms of dissolution and crystallization of amorphous glibenclamide
Amorphous solid dispersions enhance the dissolution and oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. However, the link between polymer properties and formulation performance has not been fully clarified yet. We studied the effect of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) polymers molecular weight (Mw) on the storage stability, dissolution kinetics and supersaturation stability of spray-dried amorphous glibenclamide (GLB) formulations. The solid-state stability of amorphous GLB during storage was significantly enhanced by both the 40 kDa (HPC-SSL) and 84 kDa (HPC-L) polymers, regardless of Mw differences. In contrast, HPC-SSL maintained significantly higher aqueous drug concentrations during dissolution, compared to HPC-L (its higher Mw analogue). Dedicated dissolution experiments, in situ optical microscopy and solid-state characterization revealed that aqueous drug concentrations were determined by the interplay between crystallization inhibition, drug ionization, wetting and solubilization effects: (1) HPC prevents surface nucleation, hence inhibiting crystallization, (2) intestinal colloids (bile salts and phospholipids) increase supersaturated drug concentrations via wetting and solubilization effects and (3) pH and drug ionization severely impact the degree of supersaturation. The better performance of the lower Mw HPC-SSL was due to its superior inhibition of surface crystallization during dissolution. These insights into the molecular mechanisms of dissolution and crystallization of amorphous solids provide foundation for rational formulation development.
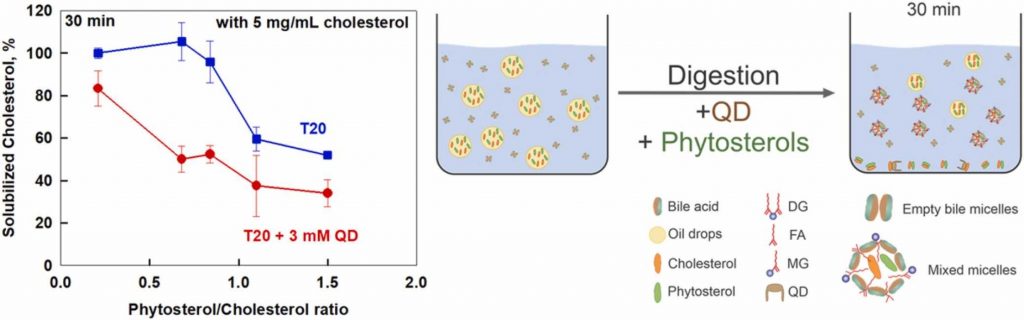
Cholesterol solubilization: Interplay between phytosterols, saponins and lipid digestion products
High plasma concentrations of cholesterol are associated with cardio-vascular disease complications and high risk of myocardial infarction. The absorption of dietary cholesterol depends on its bioaccessibility, which is in turn influenced by phytosterols, saponins and lipid digestion products. Therefore, we explored the interplay between phytosterols, Quillaja Dry saponin extract (QD), their combinations and lipid digestion on cholesterol bioaccessibility via an in vitro.