Role of food additives on properties of Polysorbate 60 solutions
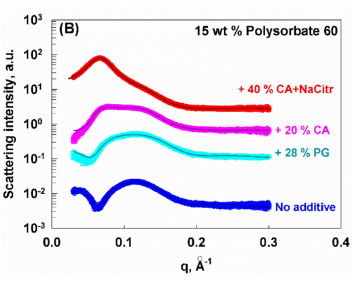
Polysorbates are hydrophilic, nonionic surfactants widely used in food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical products. Often, these emulsifiers are used in combination with different preservatives, and it is essential to conduct an in-depth study of the influence of such additives on the properties of Polysorbate 60 solutions. In the current study, we investigated the effect of various food additives: citric acid, sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, a mixture of citric acid and sodium citrate, and propylene glycol on the stability and micellar properties of Polysorbate 60 by using different experimental methods such as GC, DSC, SAXS, DLS, optical observations in polarised light, and NMR. When stored at room temperature without additives, solutions of Polysorbate 60 slowly undergo phase separation over time. Our results show that citric acid, a mixture of citric acid and sodium citrate, and propylene glycol increase the rate of this phase separation. In contrast, sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate are incorporated into the mixed micelles. They localize within the palisade layer, a region of the micelle where the surfactant tails begin, effectively preventing the phase separation. As a result, Polysorbate 60 solutions with these specific additives remain transparent and stable for over a year

