Mechanisms of drug solubilization by polar lipids in biorelevant media
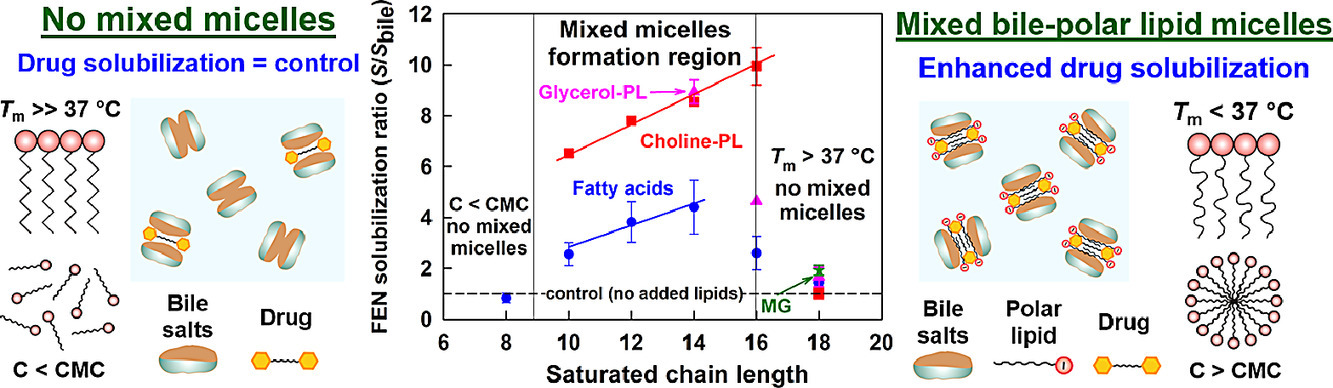
Despite the widespread use of lipid excipients in both academic research and oral formulation development, rational selection guidelines are still missing. In the current study, we aimed to establish a link between the molecular structure of commonly used polar lipids and drug solubilization in biorelevant media. The solubilization of fenofibrate by 13 phospholipids, 11 fatty acids and 2 monoglycerides was studied by an in vitro model of the upper GI tract. The main trends were verified with progesterone and danazol. It was revealed that to alter drug solubilization in biorelevant media, the polar lipids must form mixed colloidal aggregates with the bile. Such aggregates are formed when: (1) the polar lipid is used at a sufficiently high concentration (relative to its mixed critical micellar concentration) and (2) its hydrophobic chain has a melting temperature (Tm) < 37 °C. When these two conditions are met, the increased polar lipid chain length increases the drug solubilization capacity. Hence, long chain (C18) unsaturated polar lipids show best drug solubilization, due to the combination of long chain length and low Tm. Polar lipids with Tm significantly higher than 37 °C (e.g. C16 and C18 saturated compounds) do not impact drug solubilization in biorelevant media, due to limited association in mixed colloidal aggregates. The hydrophilic head group also has a dramatic impact on the drug solubilization enhancement, with polar lipids performance decreasing in the order [choline phospholipids] > [monoglycerides] > [fatty acids]. As both the acyl chain and head group types are structural features of the polar lipids, and not of the solubilized drugs, the described trends in drug solubilization should hold true for a variety of hydrophobic molecules.

