Effect of counter-ion on rheological properties of mixed surfactant solutions
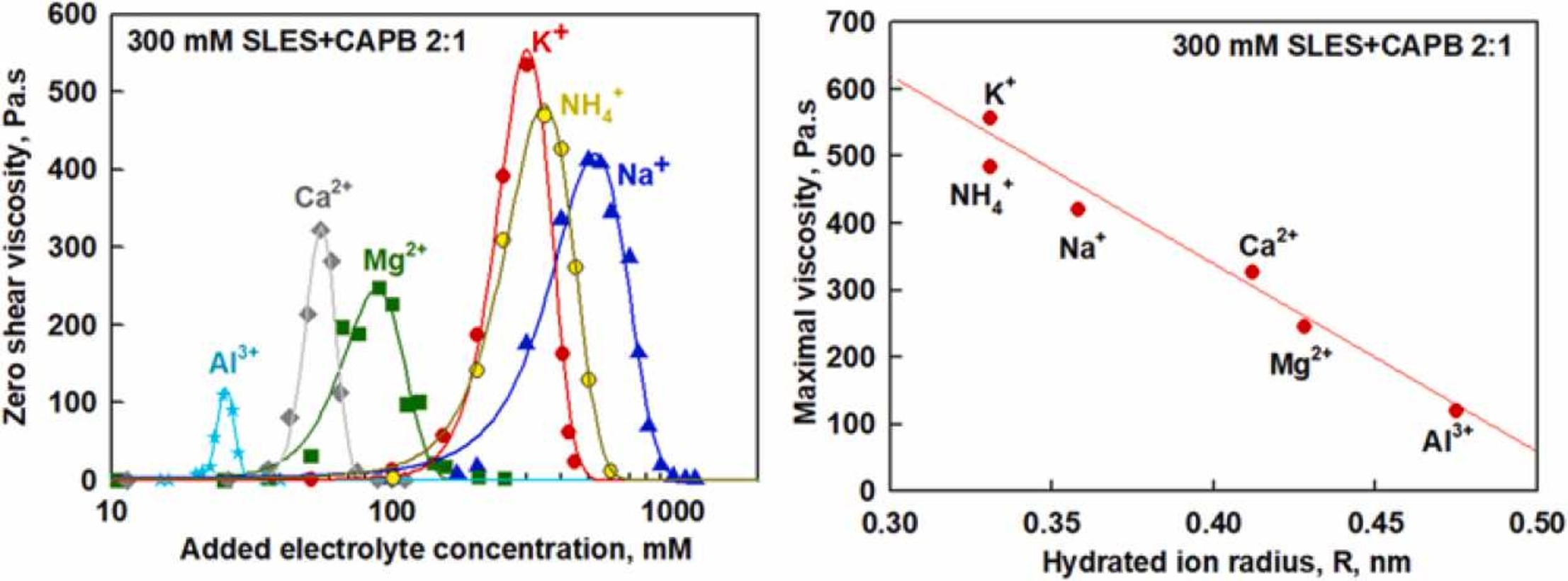
The effects of the charge, size and concentration of counter-ions (Na+, NH4+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+ and Al3+) on the rheological properties of 300 mM SLES+CAPB surfactant solutions are studied and compared with results available in the literature for the effects of Na+ and K+ on SLES solution. The results show that all counter-ions studied are able to induce formation of wormlike micelles in a certain concentration range – as a consequence, the solution viscosity passes through a high maximum as a function of salt concentration. The salt concentration leading to maximum in the solution viscosity decreases with increasing the charge density of the counter-ion, defined as the ratio of the charge of the counterion and its hydrated radius, Z/R. The maximum viscosity in the salt curve decreases with increasing the hydrated radius of the counter-ion. The addition of CAPB to SLES leads to about 10-fold higher viscosity and to higher maximum viscosity in the presence of K+ as compared to Na+, whereas the opposite trend was observed for SLES alone. These effects are attributed to the interplay between the anionic and zwitterionic surfactants, and the electrolyte in the mixed SLES+CAPB system.

