Aqueous Solutions of Oil-Soluble Polyglycerol Esters: Structuring and Emulsifying Abilities
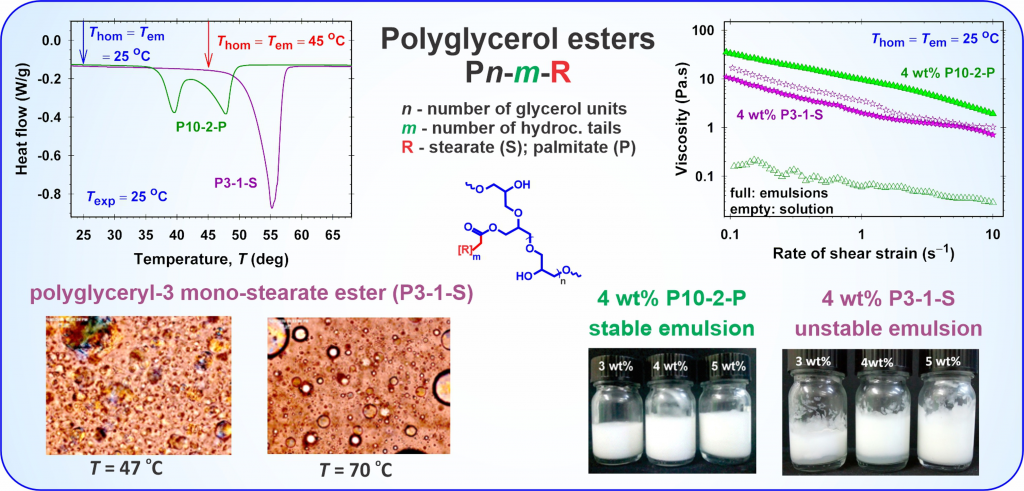
The polyglycerol esters (PGEs) of fatty acids have a wide range of HLB values and applications in diverse industries, such as pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. While the physicochemical properties of oil-soluble PGEs dissolved in oil phases are well studied in the literature, there is no information on their structuring in aqueous phases and emulsifying abilities. We combined rheological and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurements and microscopy observations to characterize the dependence of oil-soluble PGE structuring in aqueous phases on the PGE concentration, the temperature of solution homogenization, and the PGE molecular structure. Excellent correlations between the considerable changes in solution viscosity and the temperatures of the two endo- and exothermic peaks in the DSC thermograms are observed. Single-tail PGE molecules, which have a higher number of polyglycerol units, are better organized in networks, and the viscosity of their aqueous solutions is higher compared to that of the respective double-tail PGE molecules. PGEs exhibit good emulsifying ability and the viscosity of the produced emulsions at room temperature can differ by orders of magnitudes depending on the temperature of emulsification. The reported properties of oil-soluble PGEs could be of interest for increasing the range of their applicability in practice.

