Methods for studying structural properties
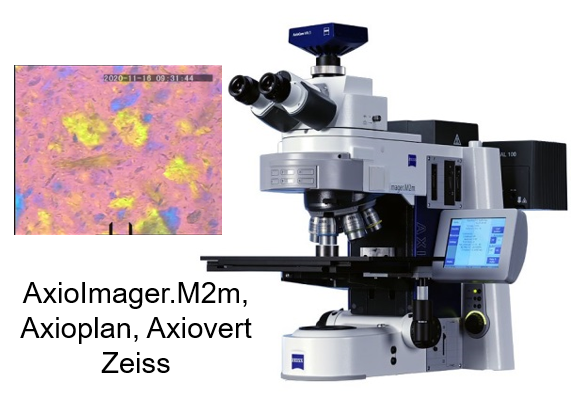
Optical microscopy
transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, polarized light

Light scattering
Particle size, Polydispersity, Particle shape, Viscosity, Molecular weight

Laser diffraction
Measuring range 0.5 – 1500 μm
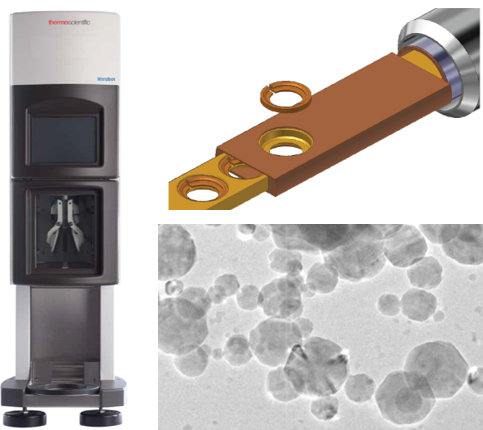

Cryo-TEM
Vitrobot
Thermo
Fisher
Scientific

SAXS/WAXS system
Xeuss 3.0, Xenocs; Detector Eiger2 R 4M Dectris
Sources: Co – 1.54 Å
& Mo – 0.71 Å
Bulk properties
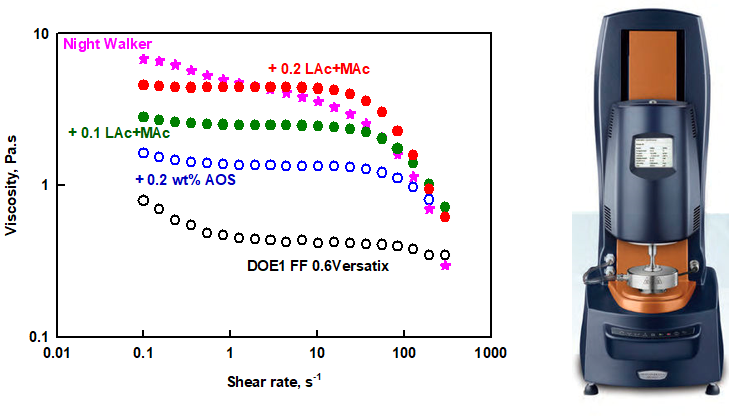
Rheometers
+optical observation; +tribology

DWS
Viscosity, Elasticity, Particle size
Mean square displacement
Mean square displacement
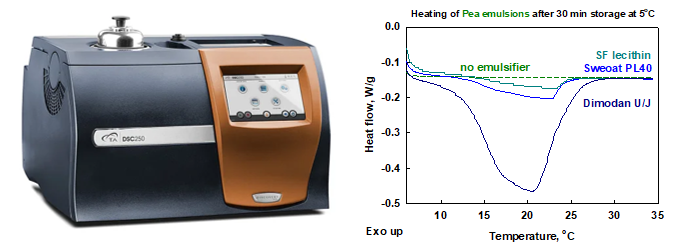
DSC
Discovery 250,
TA Instruments
Analytical techniques

Gas chromatography (GC)
Nexis GC-2030,
Shimadzu

Gel-permeation chromatography with refractive index detection
(GPC-RID)
Shimadzu
LC20AD

UPLC-PDA-ELSD
Nexera X3,
Shimadzu
Access to:
- LC-MS/MS
- Nuclear magnetic resonance 500 MHz
- Scanning electron microscope
- Atomic absorption spectroscopy
Surface properties
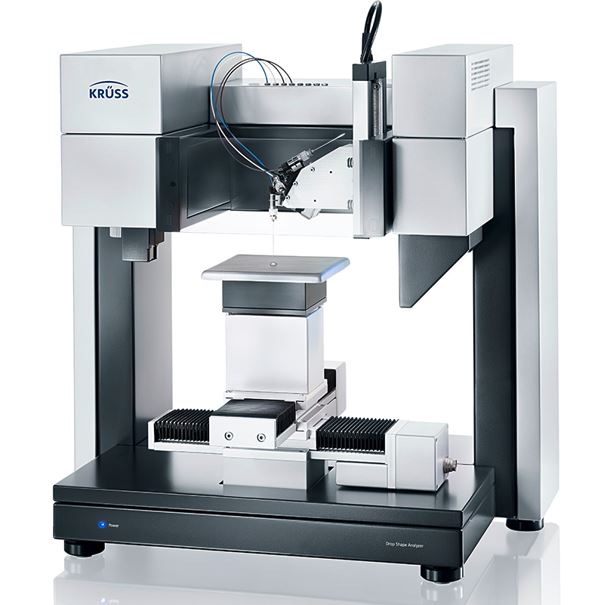

DSA 100E

BP100

K100

SDT
Equilibrium and dynamic surface/interfacial tension measurements (Krüss GmbH, Germany)

DVT

NIMA Langmuir trough

Surface shear rheology
TA Instruments
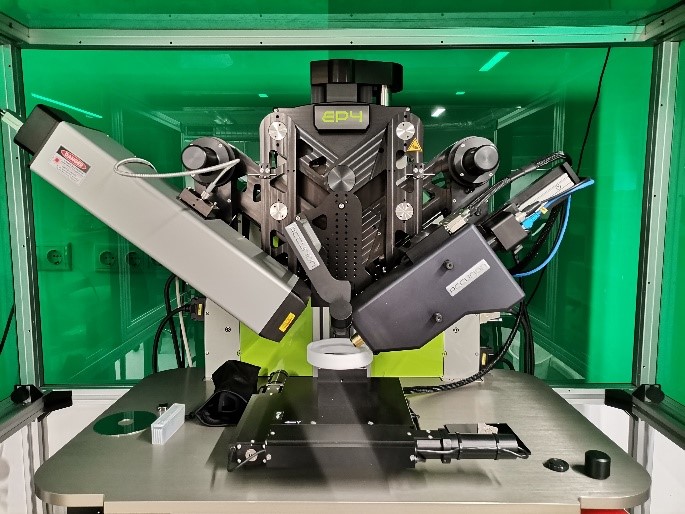
Ellipsometer with BAM
EP4, Accurion GmbH, Germany
Film properties
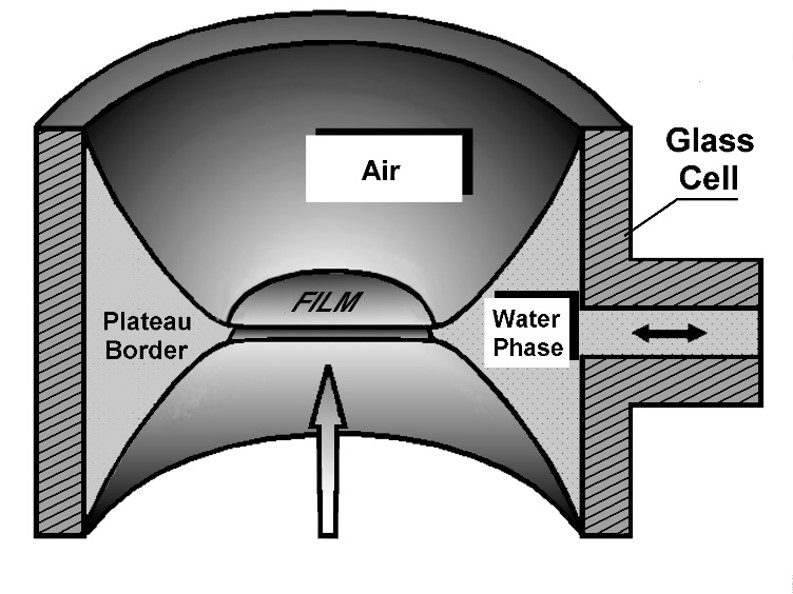
Capillary Cell
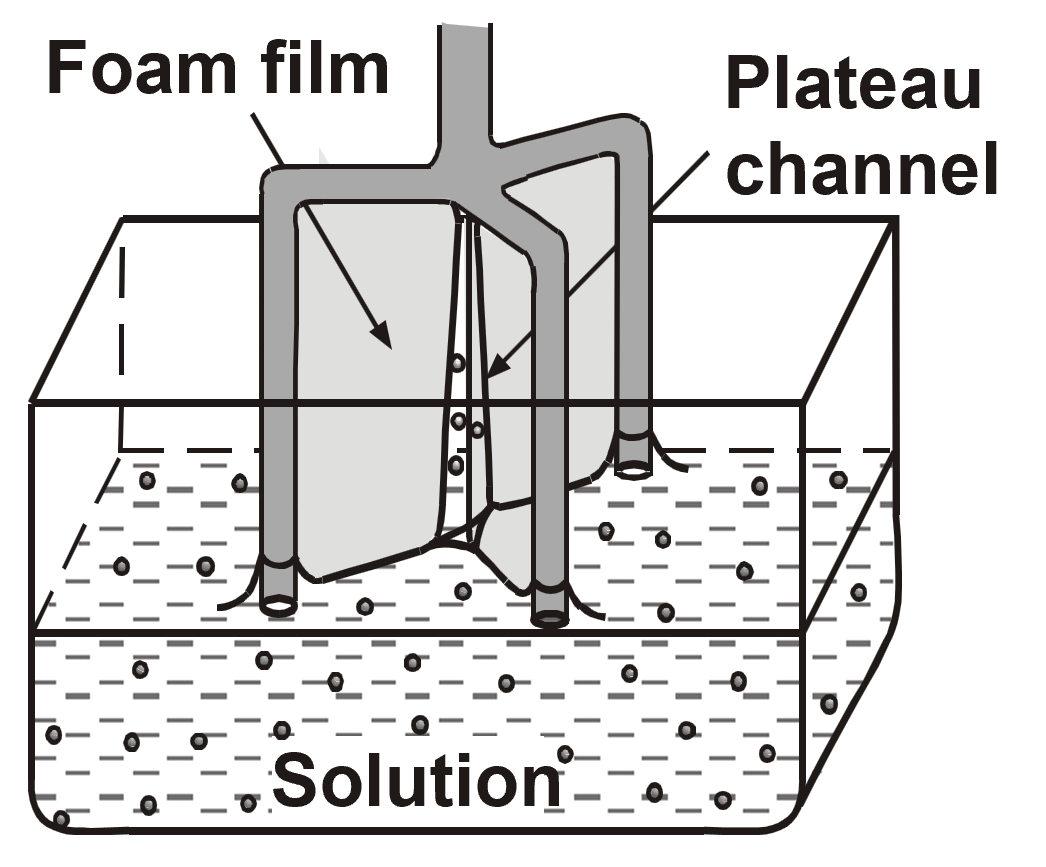
Vertical Films and Plateau channels
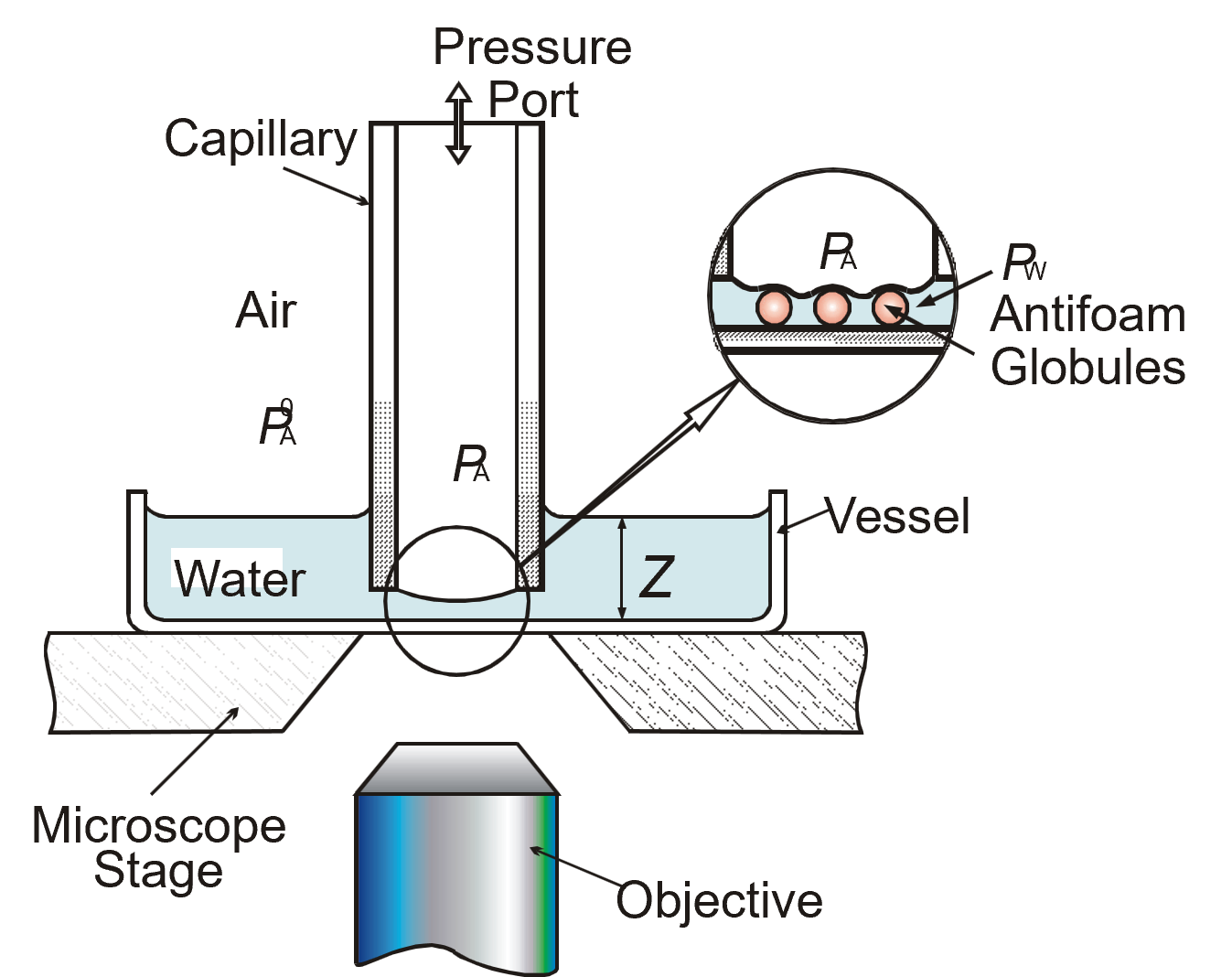
Wetting films
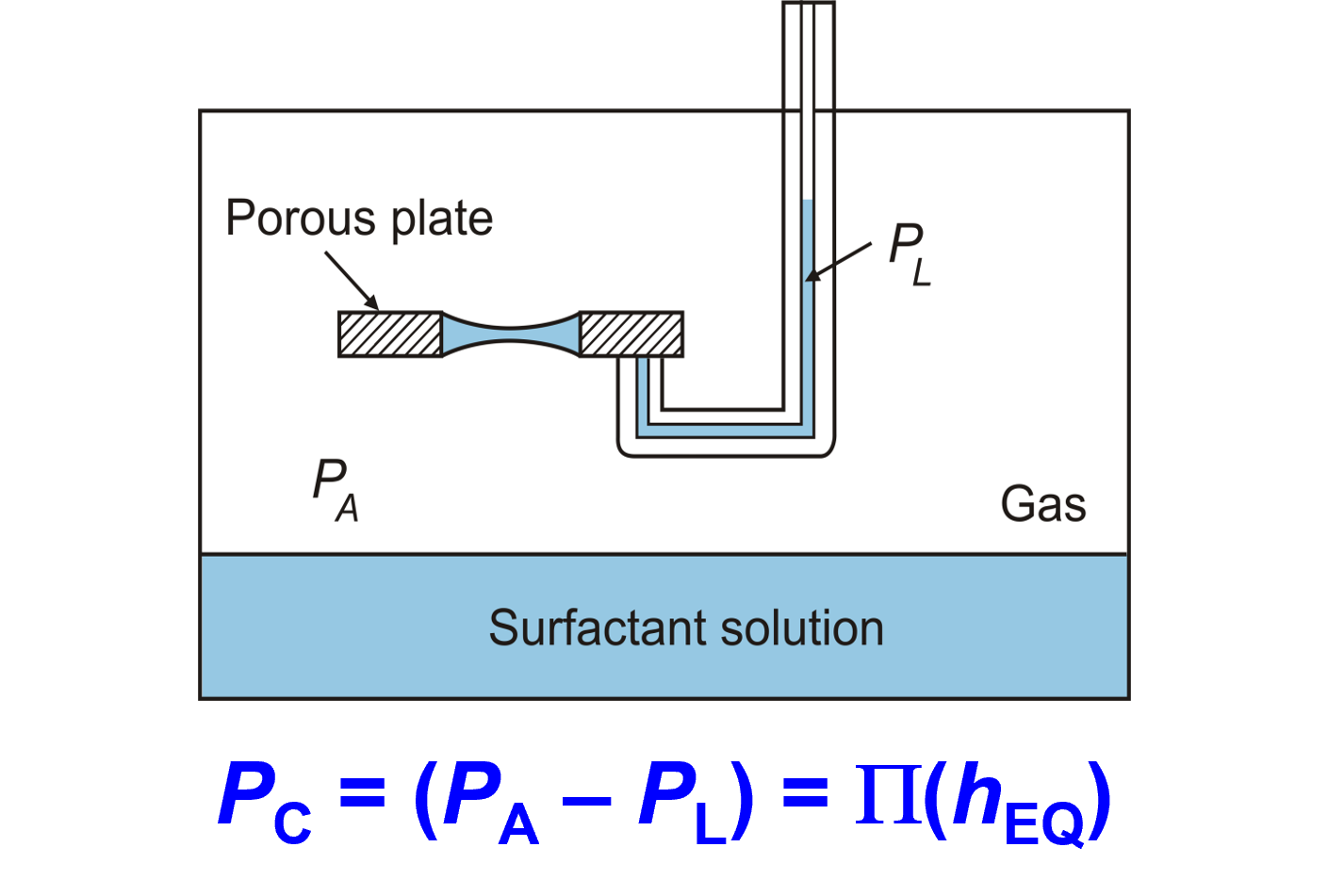
Porous plate method
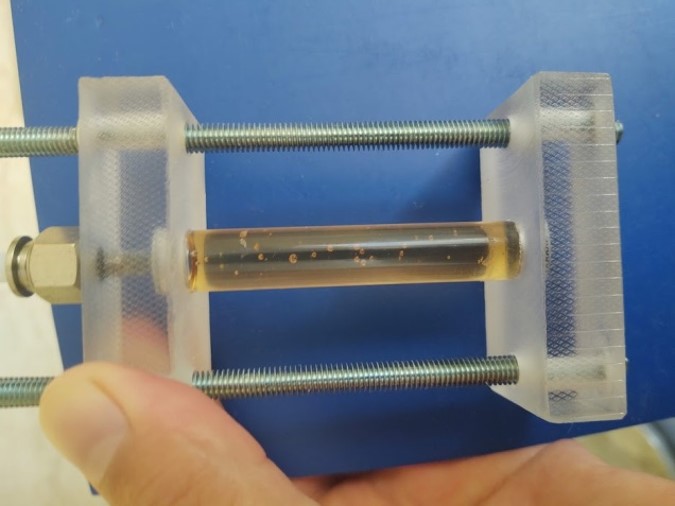
High pressure cell
Experimental set-ups for studying the behavior of single bubble or drop under large homophase are also available
Foams and emulsions

PandaPLUS 2000

Ultra Turrax

Magic Lab, IKA

Rumi RMJB-1L Vacuum Low Speed Mixer

Silverson L4RT
Gemini BV)
Emulsification methods – rotor-stator homogenizers, membrane emulsification, Magic Lab, high pressure homogenizer, narrow-gap homogenizer, etc.


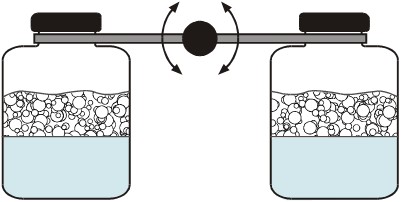
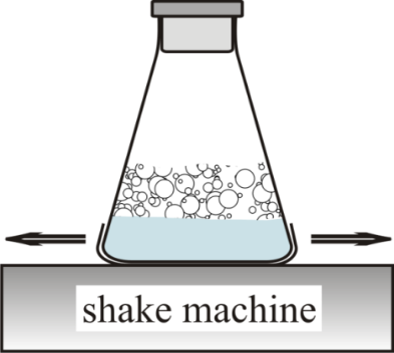
Foaming methods and analysis of foams – planetary mixers, Bartsch test, bubbling test, shake tests, etc.

