Structural and Mechanical Properties of Sodium Stearate in Glycol–Water Mixtures: Implications of Composition
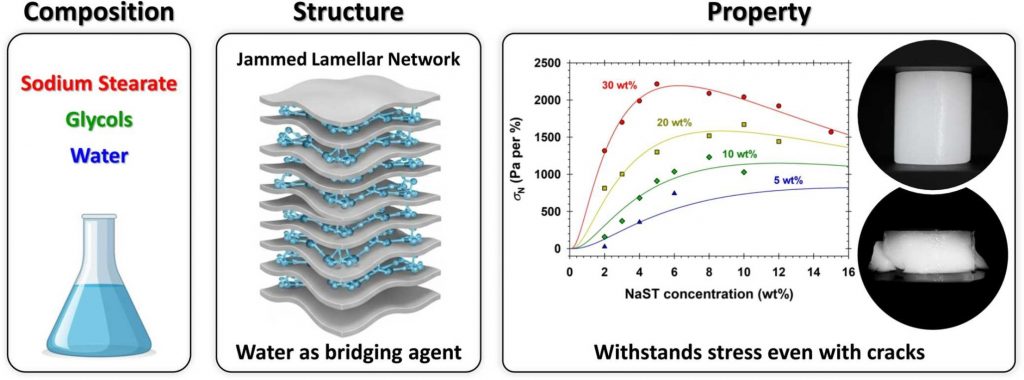
This study examines the composition–structure–property relationships of sodium stearate (NaST) formulations in propylene glycol and dipropylene glycol (PG/DPG)–water systems, focusing on the interplay between NaST concentration, water content, and mechanical performance. Using rotational rheometry, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), and mechanical testing, we demonstrate that water increases yield stress; rather than acting as a plasticizer, it promotes a jammed lamellar network. SAXS shows lamellar order persists across compositions and up to 60 ◦C, with partial melting above this. At the same time, mechanical tests reveal a transition from ductile to plastic-elastic behavior as NaST concentration increases. The formulations at 8–10 wt% NaST exhibit maximum stiffness, toughness, and ultimate strength, making them promising for high-durability applications in personal care and pharmaceutical products. These findings provide a framework for designing NaST-based materials with tailored mechanical and structural properties.

